After careful consideration I have decided to transfer all hardware review activities to a new domain. I purchased Hardwareasylum.com in 2012 and have been working hard to build a new and improved Ninjalane on that domain. If you are reading this you have reached one of the archived articles, news, projects and/or reviews that were left behind during the site migration.
Please update your bookmarks and be sure to visit the new and improved Ninjalane at Hardwareasylum.com
Eumax B605-02 Heatsink
Author: Dennis Garcia
Published: Wednesday, March 26, 2003
Benchmarks
Benchmarks
The Eumax B605-02 is designed for socket A processors including the entire AMD Athlon line up to 2800+. Here is an overview of the system and testing methodology.
Soltek SL-75MRN-L
Athlon XP2200+ Tbred (AXDA2200DKV3C)
Eumax B605-02
CoolerMaster xDream SE
I used the Soltek BIOS monitoring software to provide me with temperature information from the system. A simple game of Quake 3 provided the 100% processor usage.
Soltek SL-75MRN-L
Athlon XP2200+ Tbred (AXDA2200DKV3C)
Eumax B605-02
CoolerMaster xDream SE
I used the Soltek BIOS monitoring software to provide me with temperature information from the system. A simple game of Quake 3 provided the 100% processor usage.
Editors note: Even though the Windows XP task manager reported 100% processor usage we could never attain a 100% of the rated heat output as documented by AMD (see below) when using Quake3 as a basis for that heat production. Knowing this the game was played until the maximum temperature was attainted and stabilized, or when the round was over.
Other things to consider when judging software induced heat output.
a) Clock throttling by the processor at high temperatures.
b) Normal software isn't designed to produce maximum heat output.
c) Variances of cooling temperature.
d) Variances in CPU load.
e) Inaccuracies in thermal diode readouts.
Of course the list goes on..
My testing methodology is aimed to provide a real world look into this heatsink given the test system provided. The lower the temperature the better.
a) Clock throttling by the processor at high temperatures.
b) Normal software isn't designed to produce maximum heat output.
c) Variances of cooling temperature.
d) Variances in CPU load.
e) Inaccuracies in thermal diode readouts.
Of course the list goes on..
My testing methodology is aimed to provide a real world look into this heatsink given the test system provided. The lower the temperature the better.
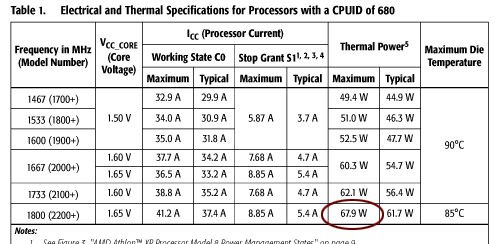

A C/W rating can quickly be calculated using this formula.
C/W = (CPU temp - Ambient temp)/(Variance(%) * CPU Watts)
Allowed variance for this test = 75%
CPU Watts = 67.9W
0.34 C/W = (42C - 24.5C)/(.75(67.9W))
C/W = (CPU temp - Ambient temp)/(Variance(%) * CPU Watts)
Allowed variance for this test = 75%
CPU Watts = 67.9W
0.34 C/W = (42C - 24.5C)/(.75(67.9W))

For this next test we cranked the FSB up to 150Mhz and re-ran the tests. To calculate how the C/W rating has changed we will need to factor in the increased processor
wattage. The formula and constants for this are listed below.
ocC/W = dCPU Watts * (ocMhz / dMhz) * (ocVcore / dVcore)2
ocMhz = 2025
dMhz = 1800
ocVcore = 1.75
dVcore = 1.65
The variance still applies for our C/W calcuation
Allowed variance for this test = 75%
ocCPU Watts = 85.55W
0.40 C/W = (50C - 24.5C)/(.75(85.55W))
You will notice the change in the C/W rating; this gives us an idea as to how well this heatsink is able to dissipate a given load. The lower this number is the better the heatsink is at cooling. We can also get an idea as to the heatsinks capacity by looking at the change in C/W in relation to CPU speed.
Keep in mind this calculation is provided for demonstration purposes only and may not reflect the actual lab tested C/W rating, but I think I'm close
ocC/W = dCPU Watts * (ocMhz / dMhz) * (ocVcore / dVcore)2
ocMhz = 2025
dMhz = 1800
ocVcore = 1.75
dVcore = 1.65
The variance still applies for our C/W calcuation
Allowed variance for this test = 75%
ocCPU Watts = 85.55W
0.40 C/W = (50C - 24.5C)/(.75(85.55W))
You will notice the change in the C/W rating; this gives us an idea as to how well this heatsink is able to dissipate a given load. The lower this number is the better the heatsink is at cooling. We can also get an idea as to the heatsinks capacity by looking at the change in C/W in relation to CPU speed.
Keep in mind this calculation is provided for demonstration purposes only and may not reflect the actual lab tested C/W rating, but I think I'm close

